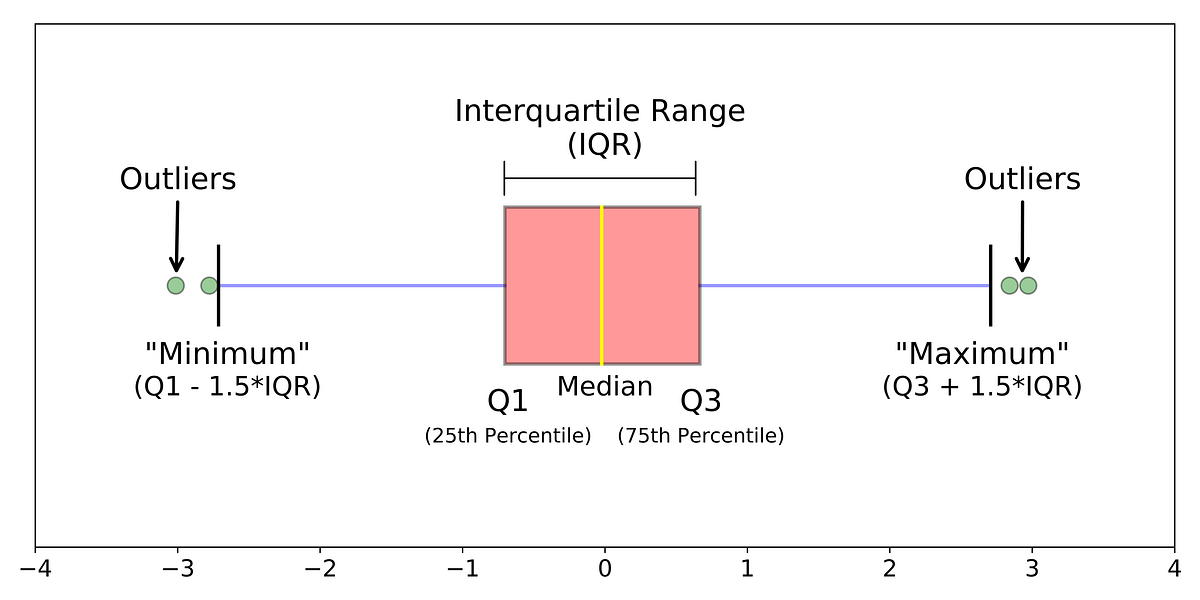
Plot box outlier boxplots detection statistics medium max
Table of Contents
Table of Contents
If you’re involved in data analysis, drawing a box plot is an essential skill to have. A box plot, also known as a box and whisker plot, is a graphical representation of the statistical summary of a distribution of data. It’s commonly used to display the distribution of different data groups and helps identify outliers, skewness, and other data characteristics. Learning how to draw a box plot is a critical tool in your data analysis toolbox.
When it comes to drawing a box plot, several challenges can arise. One key issue many people face is the interpretation of the plot’s results. Another challenge is obtaining the data that needs to be plotted. Drawing a box plot can also be time-consuming and complex, especially if you’re working with large datasets.
To draw a box plot, you first need to have your data set. Once you have your data set, you can create a box plot by dividing the data set into quarters and plotting the median, upper quartile, and lower quartile in a vertical box. You then draw a line, known as a whisker, from the top of the box to the highest data point, and from the bottom of the box to the lowest data point.
In summary, whether you’re a data analyst, statistics student, or researcher, knowing how to draw a box plot can be critical to your success. Drawing a box plot helps you identify the outliers, assess the data distribution, and draw conclusions about your data. It’s a vital skill that can be used in many data analytical applications.
How to Draw a Box Plot: A Step-by-Step Guide
As mentioned earlier, a box plot is a graphical representation of the statistical summary of a set of data, and it’s used to identify the outliers, skewness, and other data characteristics. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to draw a box plot:

Step 1: Gather your data
The first step is to gather your data. Collect your data in a spreadsheet or data management software, such as Excel or R. Ensure that your data is correctly formatted, and you have all the data points you need.
Step 2: Calculate the Median, Quartiles, and Extremes
The next step is to calculate the median, quartiles, and extremes. The median is the middle value of your dataset. The quartiles divide your dataset into four equal parts. The lower quartile (Q1) is the median of the lower half of your dataset, and the upper quartile (Q3) is the median of the upper half of your dataset. The extremes are the highest and lowest values in your dataset that are not outliers.
Step 3: Draw the Box Plot

The final step is to draw the box plot. To do this:
- Draw the box with the lower quartile, median, and upper quartile values.
- Draw whiskers from the box’s endpoints to the most extreme non-outlier values.
- Mark the outliers with individual points.
Tips for Creating Effective Box Plots
Creating an effective box plot requires care and attention to detail. Here are some tips for creating effective box plots:
Use Labels
It would help if you labeled your box plot axes clearly. Including labels ensures that anyone unfamiliar with the data who sees your graph can understand the key takeaways quickly.
Use Colors
Colors add an additional layer of meaning to your box plot, visually highlighting the data points that matter most. You can use colors to draw attention to the median, quartiles, and other data points.
Avoid Overcrowding
It’s best to avoid overcrowding your box plot with too much information. Stick to the essential data points, and use a simple design that’s easy to understand.
Question and Answer
Q: When should I use a box plot?
A: You should use a box plot when you want to analyze the dispersion, skewness, and potential outliers in a dataset. It’s ideal for identifying the variability among groups of continuous data.
Q: What are the advantages of a box plot over a histogram?
A: A box plot provides a summary of the distribution of data in a compact format. It’s easier to compare data sets side by side using box plots instead of histograms. Additionally, box plots provide a clearer picture of potential outliers in a dataset.
Q: How do I interpret outliers on a box plot?
A: Outliers are individual data points that fall outside the typical range of the rest of the data. They are displayed as individual points outside the whiskers. Outliers can be a sign of a problem or error in the data collection process or indicate that the data set contains extreme values.
Q: Can I customize my box plot?
A: Yes, you can customize your box plot to match your specific data analysis needs. You can change the colors, add titles, adjust the axis scales, remove or add gridlines, and change the font size and style.
Conclusion of How to Draw Box Plot
Box plots are a universal tool used to represent statistical data. They’re also an excellent tool for identifying the center, variability, and potential outliers of a set of data. Knowing how to draw a box plot is an essential skill that any data analyst or researcher needs. Hopefully, this guide has provided you with the knowledge and skills to create effective box plots and draw meaningful conclusions from your data sets.
Gallery
Draw Boxplot With Means In R (2 Examples) | Add Mean Values To Graph
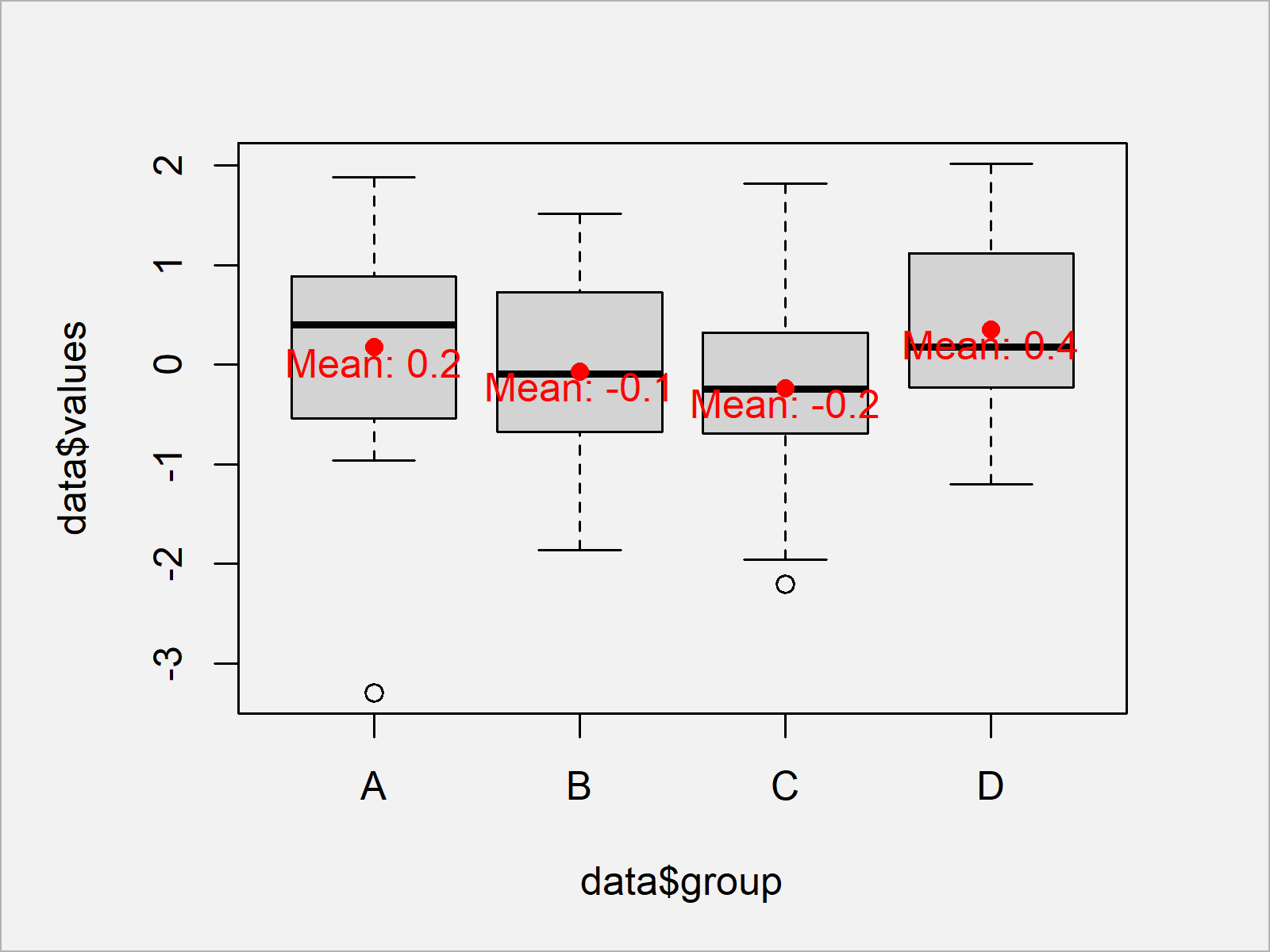
Photo Credit by: bing.com / boxplot examples whisker
박스 플롯 - IT위키

Photo Credit by: bing.com /
Outlier Detection With Boxplots. In Descriptive Statistics, A Box Plot

Photo Credit by: bing.com / plot box outlier boxplots detection statistics medium max
R - Using Plotly To Draw Boxplot For Two Groups - Stack Overflow

Photo Credit by: bing.com / boxplot plotly
Drawing A Boxplot With Pandas - VBA And VB.Net Tutorials, Education And

Photo Credit by: bing.com / boxplot pandas drawing draw fig1